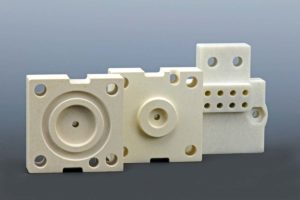
Glass Bonded Mica
Mica-Tron Products Corp. has been machining glass bonded mica since 1959. Over the decades we have machined essentially every grade of glass bonded mica produced in North America and in Europe. We also have considerable experience machining both natural mica grades and synthetic mica grades. Because of our half century of machining glass bonded mica, we have attained the utmost expertise in producing glass bonded mica components. We have developed proprietary techniques and tools which allow us to machine parts that other fabricators will not even attempt.
In addition, our experience and equipment allow us to machine glass bonded mica parts in sizes that range from micromachined to sizes that are as large as the maximum sheet sizes available.
We have the experience and knowledge that allows us to help engineers and designers produce parts in the most efficient and economical manner, and we can offer suggestions regarding part design and cost effectiveness.
Our capabilities include CNC turning, CNC drilling, CNC milling and CNC grinding of all glass bonded mica grades.
Glass bonded mica, commonly known by the trade names Mycalex®, Mykroy®, Supramica®, and Arclex®, is one of the oldest high performance materials in existence, having been in commercial use since 1921.
Glass bonded mica is composed of finely powdered electrical grade glass and precisely-sized mica flakes, natural or synthetic. The glass/mica mixture is pressed into a preform which is then heated to make the glass flow, after which the preform is compression molded into sheet form. This process creates a new composition with all the insulating properties of both the glass and the mica. During the process, the glass flows around the mica and solidifies under pressure into a single mass. The process is carefully monitored in order to halt the process at the point where the glass begins to alloy with the edges of the mica, hence preserving the mica identity which, in turn, retains the excellent dielectric properties of the mica.
The term “ceramoplastic” was given to glass bonded mica due to the material’s ability to be processed in a fashion similar to organic thermoplastics; that is, it can be machined or injection molded, while at the same time possessing many of the desired characteristics of ceramics.
TEMPERATURE
The upper, continuous service temperature of organic plastics in an oxidizing atmosphere currently lies in the 500° to 600°F range (260° to 315°C). Most organic plastics are not dimensionally stable and are affected by moisture, thermal cycling, thermal expansion, irradiation, and age. Glass bonded mica parts can operate continuously at temperatures ranging from 750° to 1650°F, depending on the grade of material. Even at elevated temperatures, glass bonded mica is extremely dimensionally stable and can withstand thermal cycling and nuclear radiation.
Glass bonded mica can also be used in cryogenic applications. At the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratories, tests performed at temperatures of -450°F indicated that the material maintained its integrity, even at that extremely low temperature.
THERMAL
Glass bonded mica has a coefficient of thermal expansion which approximates many metals, thus making it easier to design insulator/metal assemblies that operate over a wide temperature range. Because glass bonded mica has low thermal conductivity, it makes an excellent thermal insulator. It can also withstand thermal cycling while still maintaining dimensional stability.
DIELECTRIC STRENGTH
Dielectric strengths average about 350 volts per mil for specimens 1/8 of an inch thick. The materials exhibit resistance to arcing, are non-tracking and are non-combustible.
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
- Aerospace/Defense
- High Vacuum applications, does not outgas
- Semiconductor instrumentation
- IC test sockets
- Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry
- Cryogenic applications
- Arc chutes/Barriers
Mycalex®, Mykroy® and Supramica® are registered trademarks of Crystex Composites LLC
Arclex® is a registed trademark of Tenmat Ltd